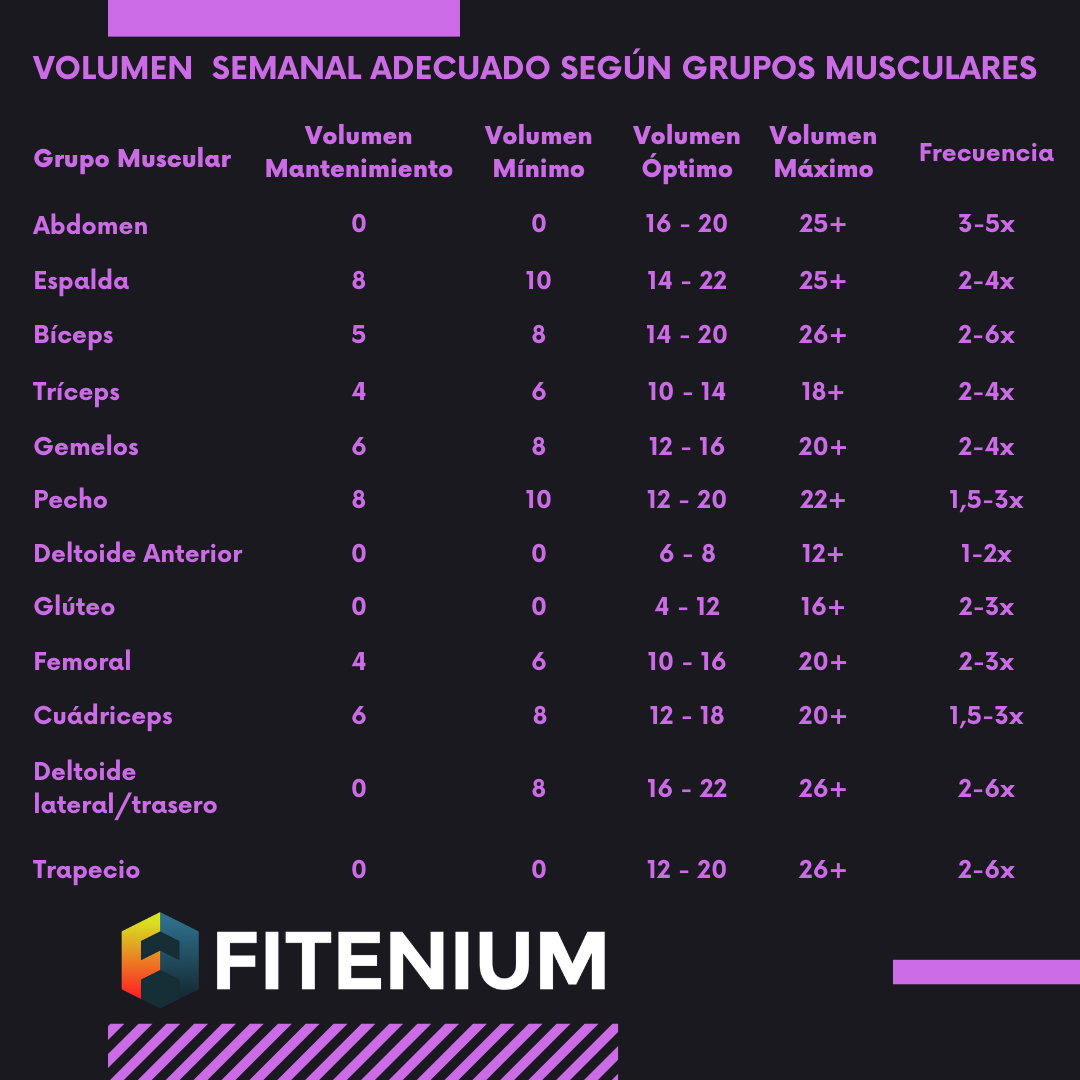
What to eat to gain muscle mass
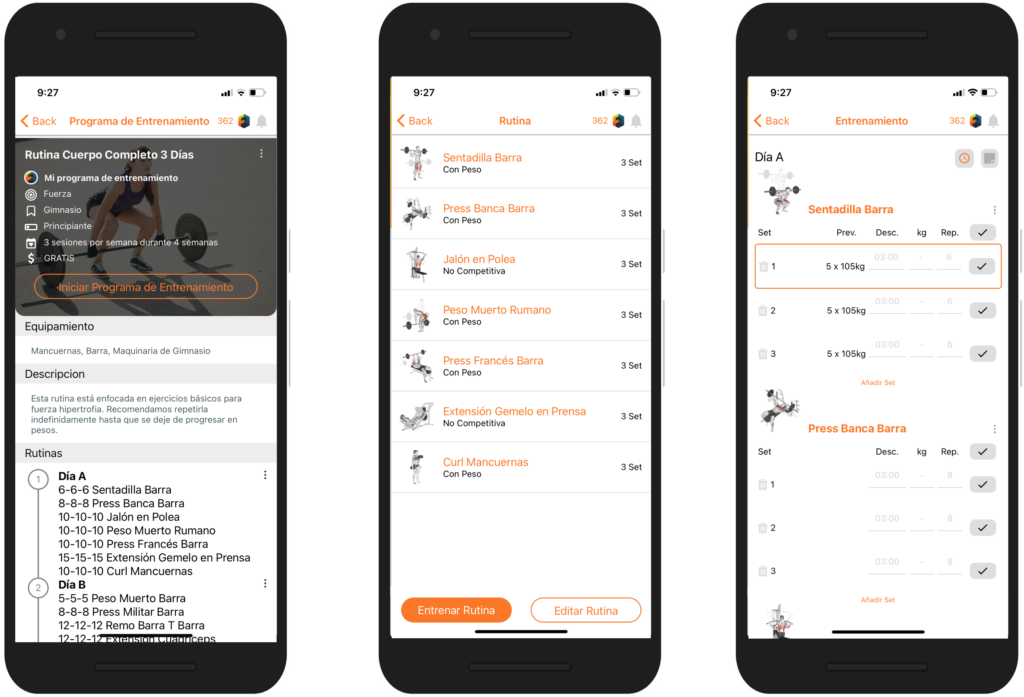
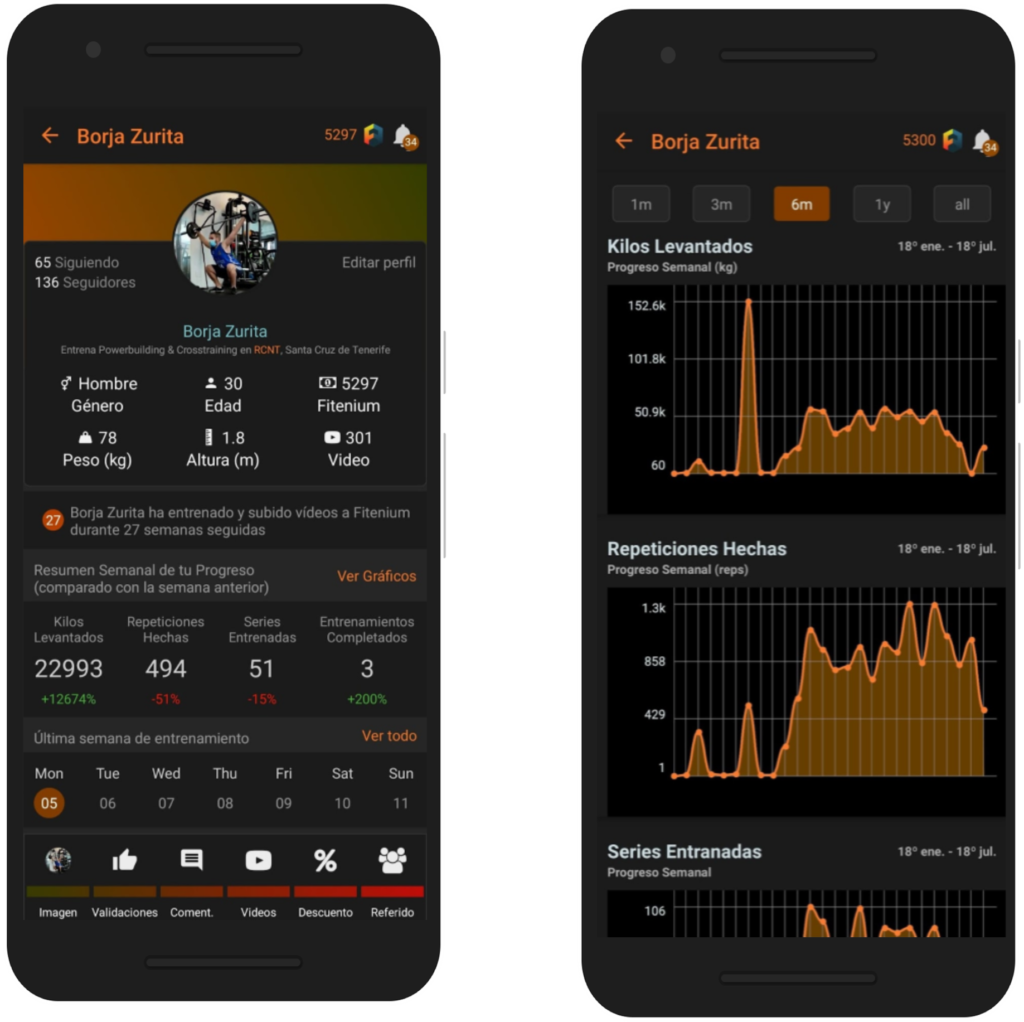
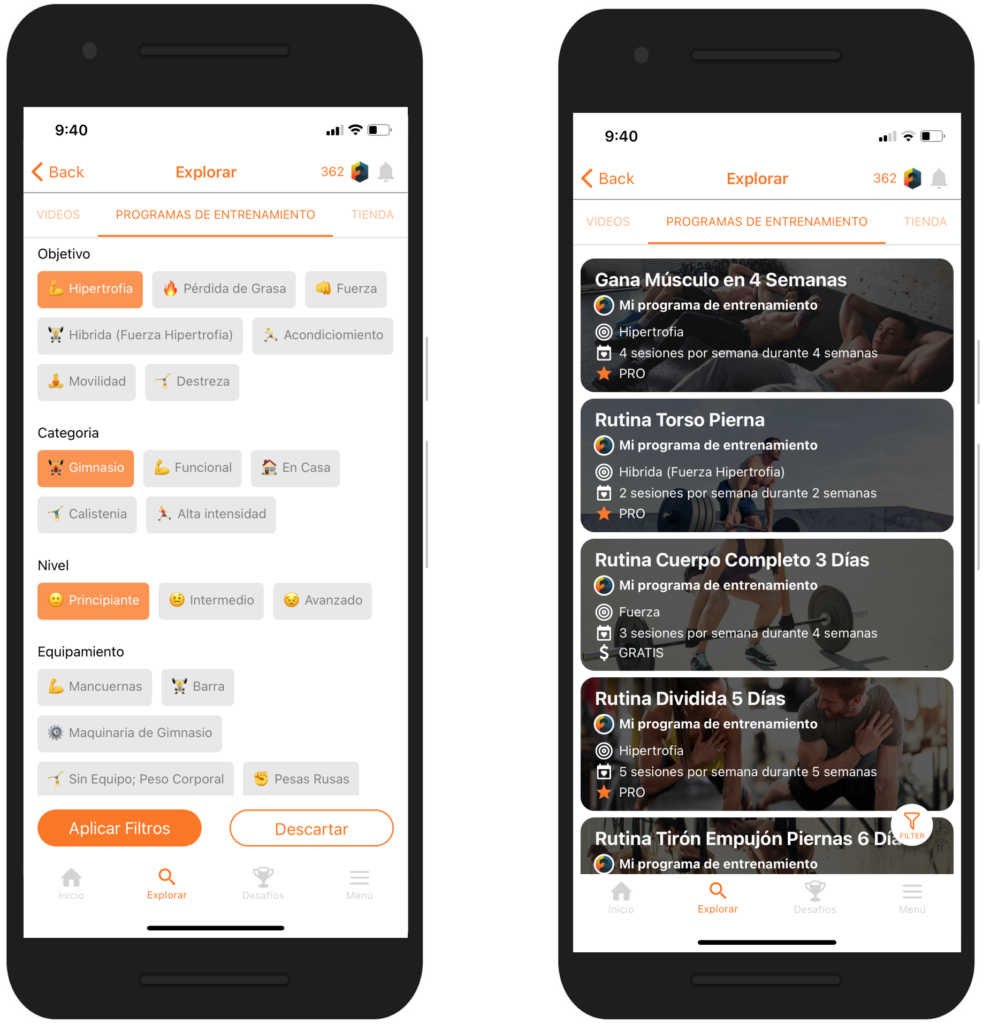
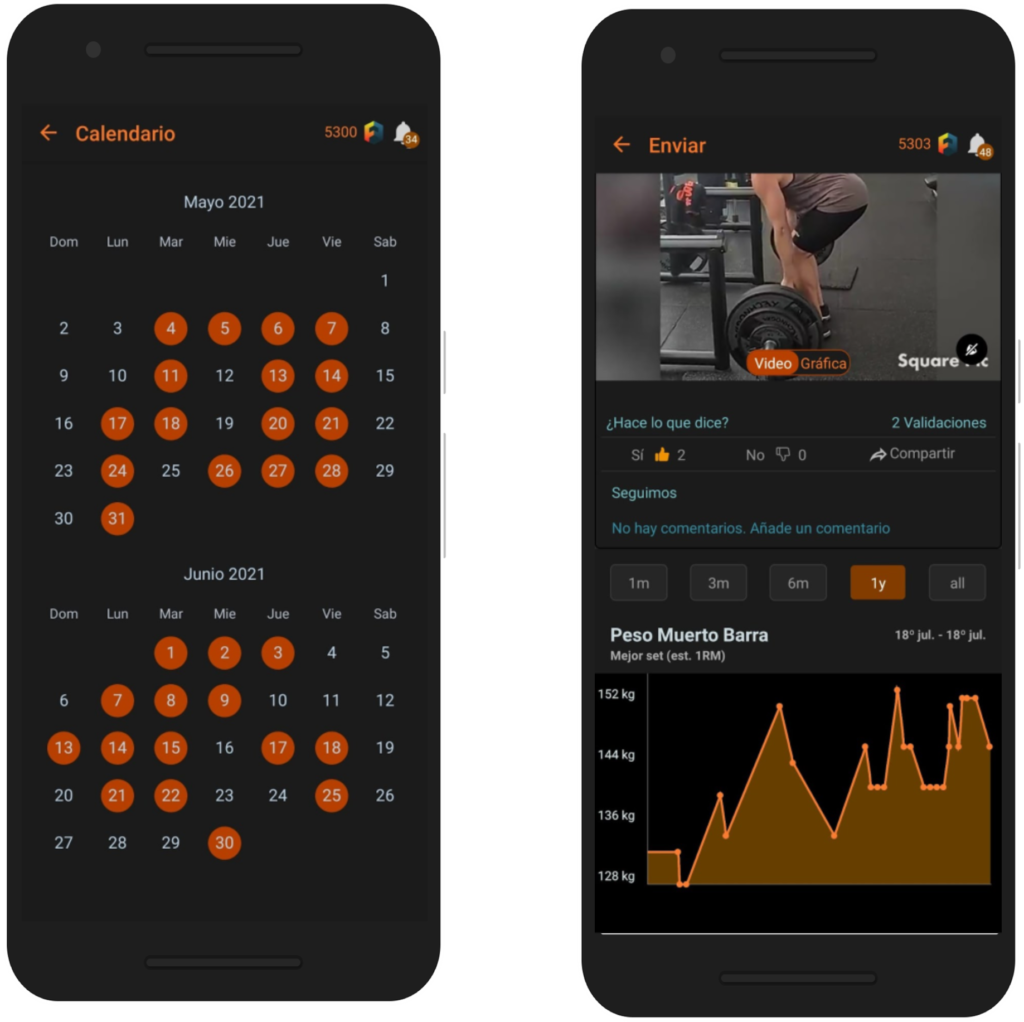
If you don’t already know Fitenium is a free, mobile, video-based social network for athletes who train strength or bodyweight exercises. At Fitenium users can follow their performance, compete and get discounts in nutrition and sports equipment stores. Download it here.
It is common to read that gaining muscle mass is a marathon. A volume phase is an exercise in perseverance and patience, since it takes a long time to see results compared to a definition phase. If you are also one of those people who have difficulty gaining weight, it can be frustrating. That’s why after weeks of eating a healthy hypercaloric diet with barely a sight of the scale moving, it’s quite tempting to go to the first fast food restaurant you see and bump up your calories. However, there are better options to build muscle mass, being rich in nutrients and dense in calories.
If you make a conscious effort to include these foods in your diet you will see how the number of calories goes up easily while you eat healthy and delicious meals.
First of all, how much should I eat to gain muscle mass?
We must be clear that both to lose fat and to gain muscle mass, more does not mean better. Creating a larger caloric deficit in your diet will slow your metabolism and make your trim unsustainable, and in the muscle gain phase the same principle applies. We must create a caloric surplus as a basis to gain muscle mass, but the surplus must be controlled to minimize fat gain, which on the other hand is inevitable, and therefore, maximize muscle mass gain and not have to do aggressive definitions later . This study analyzes the limit that the body has to gain muscle mass, with the rest of the caloric surplus going to our fat reserves
To find out how many calories we should consume to gain muscle mass, we will go to a basal metabolism calculator and enter our data to have an estimate of our daily caloric expenditure, including our physical activity. However, we must be careful with this calculator, since formulas like Harris Benedict tend to overestimate the exercise quite a bit.
For example: we are a person of 30 years, 180 centimeters and 70 kilos of weight. We have a sedentary job and we train 6 times a week. We enter the data in the basal metabolism calculator and obtain these results.

Another simpler and valid option for people who do sports at a recreational level, recommended by Lyle Mcdonald, is simply multiplying your weight in pounds by 11. Adapting it to kilos would be multiplying your body weight by 26-28. This result is usually quite accurate when calculating the caloric expenditure of a person with an average composition who trains regularly.
For example: a recreational athlete weighing 83 kilos would obtain a result of 1,890 by multiplying his weight by 27. Adding a caloric surplus of 400 calories, we would get a goal of 2,290 calories per day. It is surprising how similar this data is compared to that of the calculator considering its simplicity, but the truth is that it is a good starting point.
Maintain muscle mass gain over time
We have already determined our caloric intake, and we will progress in our weight over the weeks and months. The reasonable thing to do in a volume phase if we want to prioritize gaining muscle mass is to gain between 500 grams and 1 kilo every four weeks. The changes in our weight are not linear, so we recommend weighing yourself every day and taking a weekly average that we will take as a reference.
At some point, we will gradually stop gaining weight and reach a point of stagnation. It is reasonable because a 70-kilo person does not consume the same calories as a 80-kilo person and what was a caloric surplus will cease to be over time. At this point we simply add 100 calories to the diet while maintaining our macronutrient allocation. If we continue to stagnate, another 100 calories.
It is important that the rise in our caloric intake is progressive to focus on gaining muscle mass and minimizing fat gain.
macronutrient distribution
Although the star macronutrient in fat loss is protein, when we want to gain muscle mass, carbohydrates take on a lot of prominence. That does not mean that a good diet to gain muscle mass does not have a higher amount of protein than the average sedentary person.
Regarding protein, the recommendation for people who do weight training is between 1.8 and 2.5 grams of protein per kilo of weight. If we are in the definition phase we should go towards the upper end and in the volume phase to the lower end, since there is not so much danger of catabolism. Therefore, we will take as a base 1.8 grams of protein per kilo of weight. Each gram of protein is equivalent to 4 calories.
Fats are important to have an adequate hormonal environment to gain muscle mass, so we should not minimize them. In addition, each gram of fat is equivalent to 9 calories, so it is good to put more calories in our diet if it is difficult for us to reach the calories. A reasonable recommendation is 0.7 grams of fat for each kilo of weight.
Carbohydrates are very important in this phase, since they will give you energy to perform better in your workouts and are less satiating than protein, which helps us increase daily caloric intake. Since we have already calculated our total calories, and we know how many grams of protein and fat we are going to consume daily, our carbohydrate intake will simply be the rest of the calories we have!
Continuing with the example of the 30-year-old athlete and 70 kilos who has 2,390 calories a day as a goal.
- 1.8 grams of protein per pound of weight = 126 grams of protein * 4 calories per gram = 504 calories.
- 0.7 grams of fat per pound of weight = 49 grams of fat * 9 calories per gram = 441 calories.
- 2,390 total calories – 441 calories from fat – 504 calories from protein = 1,445 calories from carbs divided by 4 calories per gram = 393 grams of carbs.
This results in a diet with the following distribution of macronutrients: 21% protein, 19% fat and 60% carbohydrates.
Recommended foods to gain muscle mass
Interesting foods in a muscle gain diet usually have a series of characteristics that define them: caloric density, nutritional density and good distribution of macronutrients. Our list of recommended foods with your is as follows:
- Salmon: per 100 grams 191 calories, 20.6g of protein, 12g of fat and 0g of carbohydrates.
- Chicken thighs: per 100 grams 114 calories, 19g of protein, 4.1g of fat and 0g of carbohydrates.
- Lean pork: per 100 grams 156 calories, 22g of protein, 7.6g of fat and 0g of carbohydrates.
- Serrano Ham: per 100 grams 221 calories, 28g of protein, 12g of fat and 0.2g of carbohydrates.
- Cured sheep cheese: per 100 grams 450 calories, 23g of protein, 39g of fat and 1.8g of carbohydrates.
Why are all the above products interesting? All of these foods are sources of highly bioavailable protein, high-quality fats, and are very nutritionally dense.
- Tuna in Olive Oil: per 100 grams 147 calories, 13.52g of protein, 10.8g of fat and 0g of carbohydrates.
- Natural Almond: per 100 grams 602 calories, 25.3gr of protein, 50.9gr of fat and 5.4gr of carbohydrates.
- Cashew: per 100 grams 604 calories, 21.9g of protein, 48.2g of fat and 19g of carbohydrates.
- Peanut Butter: per 100 grams 562 calories, 24.2gr of protein, 44.6r of fat and 15.9gr of carbohydrates.
- Avocado: per 100 grams 160 calories, 2g of protein, 14.66g of fat and 8.53g of carbohydrates.
- Olive Oil: per 100 grams 884 calories, 0g of protein, 100g of fat and 0g of carbohydrates.
Why are all the above products interesting? They are products quite high in healthy fats and calories, which is why, in moderation, they are ideal for reaching our target calories in volume diets.
- Oatmeal: per 100 grams 367 calories, 12.1g of protein, 8.4g of fat and 56.1g of carbohydrates (1.0g of sugar).
- Banana: per 100 grams 89 calories, 1.09g of protein, 0.33g of fat and 22.84g of carbohydrates.
- Potato: per 100 grams 104 calories, 1.66g of protein, 2.4g of fat and 19.36g of carbohydrates.
- Sweet Potato or Sweet Potato: per 100 grams 107 calories, 1.61g of protein, 0.6g of fat and 24.19g of carbohydrates.
- Whole milk: per 100 grams 146 calories, 7.86g of protein, 7.93g of fat and 11.03g of carbohydrates.
Why are all the above products interesting? They are slow assimilation carbohydrates, perfect for energy without sugar spikes.
conclusions
The most important thing to take away from this article is that gaining muscle mass is a long-distance race. Do not despair and the results are less noticeable than when you start a phase of fat loss. We must not get carried away with the “more is better” and apply too large a surplus because that will increase fat gains. We must not forget clean foods that are valid for both definition and volume phases, but we can also prioritize foods with a little more caloric density as long as that density is accompanied by healthy ingredients and nutritional density.
If you follow this plan consistently, the results will come. And we want you to share them in Fitenium.